which radiographic test shows soft tissue best|different types of radiology tests : online sales A CT scan may be recommended if a patient can’t have an MRI. People with metal implants, pacemakers or other implanted devices shouldn’t have an MRI due to the powerful . See more Resultado da Trasmissão ao vivo da XXXTreme Lightning Roulette da Evolution com resultados ao vivo e estatísticas rastreadas em tempo real. Não é necessário fazer login.
{plog:ftitle_list}
21 de jan. de 2022 · 二、ANOSIM原理简介. ANOSIM [2] (Analysis of similarities)是在1993为解决多物种丰度数据的普遍适用性,而开发的非参检验,至今已被引用14285次,在群落多样性研究中极具权威性。. 首先,通过变量(物种/OTU等丰度信息)进行样本关系计算,得到距离矩阵(图2 a .
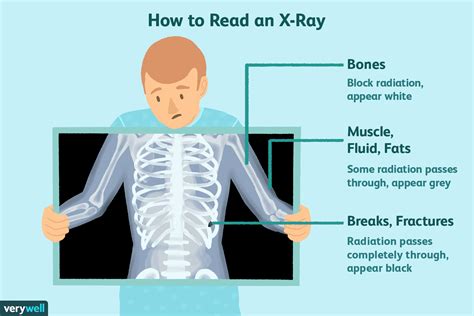
An X-ray, also called a radiograph, sends radiation through the body. Areas with high levels of calcium (bones and teeth) block the radiation, causing them to appear white on the image. Soft tissues allow the radiation to pass through. They appear gray or black on the image. An X-ray is the fastest and most accessible . See moreAn MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, uses a powerful magnet to pass radio waves through the body. Protons in the body react to the energy and create highly detailed pictures of the body’s structures, including soft tissues, nerves and blood vessels. Unlike X . See moreA CT scan, or computed tomography scan, sends radiation through the body. However, unlike a simple X-ray study, it offers a much higher level of detail, creating computerized, 360-degree views of the body’s structures. CT scans are fast and detailed. They . See more
A CT scan may be recommended if a patient can’t have an MRI. People with metal implants, pacemakers or other implanted devices shouldn’t have an MRI due to the powerful . See more
types of x ray tests
Optimizing the MRI Protocol. The objective of preoperative MRI of a soft-tissue lesion is to maximize the information gained with the least amount of patient time and discomfort. Insofar as possible in the clinical setting, the . CT scans use a series of x-rays to create cross-sections of the inside of the body, including bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. What to expect: You will lie on a table that slides into the scanner, which looks like a .The MRI tool uses magnetic fields and a sophisticated computer to take high-resolution pictures of your bones and soft tissues. In this cross-section MRI scan of a tibia (shinbone), a bone tumor shows up clearly as bright white against .MRI is the most accurate modality for diagnosing soft tissue masses because it can provide further information regarding adjacent anatomic structures, presence of necrosis, border definition,.
This radiographic appearance (calcified soft-tissue mass) in context of slowly growing juxtaarticular mass in young adult strongly suggests appropriate diagnosis of synovial sarcoma. In addition, radiographs are the best initial .Variant 2: Radiography is usually appropriate for the initial imaging of a nonsuperficial (deep) soft tissue mass. Variant 3 : MRI without and with IV contrast is usually appropriate as the next imaging study for a soft tissue mass following nondiagnostic radiographs or . A: Axial conventional T2-weighted (TR/TE; 1800/80) spin-echo MR image shows well-defined, nonspecific, soft tissue mass (asterisk). B: Corresponding radiograph shows peripheral and central calcification. The .
Radiologic evaluation of musculoskeletal soft-tissue masses has changed dramatically with the continued improvements in imaging technology. The integration of advanced imaging has provided the radi. Key Results. This consensus statement reviews US features of soft-tissue masses, providing recommendations for diagnosis and care. If a soft-tissue mass is superficial, there is a group of common diseases that have . Radiographic features Plain radiograph. X-rays are generally of limited value for the evaluation of a soft tissue abscess but they might show soft tissue gas or foreign bodies increasing suspicion for an infectious process or reveal any other causes for underlying soft tissue swelling 2.
Plain Films. The initial choice for foreign body detection is plain film radiography, which is the imaging modality of choice due to its ability to detect most foreign bodies quickly and cheaply with relatively low radiation exposure. . Plain radiography has a limited role in the management of sinusitis. . MRI is only used to differentiate soft-tissue structures, such as in cases of suspected fungal infection or neoplasm .
Technical note Ultrasound compared with projection radiography for the detection of soft tissue foreign bodies e A technical note H. Grocutt a, R. Davies b, C. Heales b, * a Royal Cornwall Hospitals NHS Trust, Treliske, Truro, TR1 3LJ, United Kingdom b University of Exeter, St Luke's Campus, Heavitree Road, Exeter, EX1 2LU, United Kingdom article info>Radiation field size:-12 inches (30 cm) lengthwise and 1 inch (2.5 cm) beyond the skin line on the sides, but not more than 10 inches (24 cm) >Patient position: Upright or supine > Part position: - MSP centered perpendicular midline of the grid - Adjust the patient's shoulders to lie in the same transverse plane. - Extend the patient's neck slightly >Central ray (CR): - Perpendicular .Advanced imaging is often needed for diagnosis following plain film radiography, because 50% to 75% of the bone matrix must be destroyed before lytic changes are evident on plain radiographs. 22 .
The ankle joint is one of the most commonly injured joints and the most common type of fracture to be treated by orthopedic surgeons.[1] The estimated incidence of ankle fractures is approximately 187 per 100,000 people per year.[2] It appears that the incidence of these fractures is increasing in developed countries, presumably secondary to the increasing . INTRODUCTION. The knee is one of the largest and most complex joints in the body. It is lined by synovium and consists of two hinge-type joints between the femoral condyles and the medial and lateral tibial plateaus and of a gliding-type joint between the patella and the trochlear groove of the anterior distal femur () [].The major stabilizers of the joint are the .
Conventional radiography only provides a measure of the X-ray attenuation caused by an object; thus, it is insensitive to other inherent informative effects, such as refraction. Furthermore, conventional radiographs are degraded by X-ray scatter that .Soft-tissue sarcomas, unlike benign soft-tissue lesions, are relatively uncommon and are estimated to represent about 1% of all malignant tumors [15, 16].Hajdu [] noted that the incidence in the United States is about the same as that of multiple myeloma or carcinoma of the thyroid.Soft-tissue sarcomas are two to three times as common as primary malignant bone .
Soft tissue injuries (e.g., whiplash, sprains, strains, and tears) are very commonly the result of automobile accidents. However, because soft tissue injuries involve damage to discs, muscles, ligaments, and tendons, they can be difficult to spot and diagnose. Here are some common tools treatment providers can use to diagnose soft tissue injuries:
Editor’s Note: Read Radiographic Soft Tissue Positioning: Part 2 here. A thorough understanding of the factors that influence diagnostic radiography can help veterinary nurses obtain radiographs that allow for both accurate diagnoses and proper treatment plans for patients. Patient positioning is an important factor that can drastically affect radiographic .Soft tissue/fluid. Both soft tissues and fluids have the same radiopacity. This is the radiopacity of normal soft tissue and fluid-filled organs (heart, liver, spleen, urinary bladder). Variation in volume, thickness and degree of compactness of soft tissue creates a pattern of various densities on the radiograph Fat. Look for structural problems in your bones, joints or soft tissues. Plan and evaluate treatments. What can an X-ray show? Issues that can show up on X-rays include: Arthritis. Broken bones. Bone changes or abnormalities. Herniated discs in your spine. Infections. Kidney stones. Scoliosis and other spine curvature conditions. Tooth cavities. Tumors.It is best diagnosed by CT with IV contrast or MRI and treated with early broad-spectrum antibiotics and surgical intervention. . Conventional radiography shows a soft-tissue density mass causing sinus cavity expansion, .
The value of retropharyngeal soft tissue measurements in trauma of the adult cervical spine. Cervical spine soft tissue measurements. Skeletal Radiol. 1987;16:98–104. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Costelloe CM, Madewell JE. Radiography in the initial diagnosis of primary bone tumors.Define the medical term venography. - the technique of mechanically widening a narrowed or obstructed blood vessel - a radiographic test that provides an image of specific veins after a contrast dye has been injected - uses computer assistance to clarify the view of the area of interest in the cardiovascular system by "subtracting" the soft tissue and bones from the .A regular x-ray of the area with the lump may be the first test ordered. A chest x-ray may be done after you are diagnosed to see if the sarcoma has spread to the lungs. . It can show your health care team many things about the tumor, like where it is, how big it is, and sometimes even the type of tissue it comes from (like bone, fat, or .
different types of radiology tests
Different parts of the body absorb the x-rays in varying degrees. Dense bone absorbs much of the radiation while soft tissue (muscle, fat, and organs) allow more of the x-rays to pass through them. As a result, bones appear white on the x-ray, soft tissue shows up in shades of gray, and air appears black. This document discusses techniques for visualizing soft tissues in radiography. Soft tissues have less differential attenuation compared to bones, making contrast reduced. Special techniques are needed to improve contrast and demonstrate soft tissues clearly. These include adjusting the kVp and adding filters to change image contrast. Ultrasonography can detect radiolucent materials (e.g., wood, vegetation) better than radiography and computed tomography. 8, 9 Hyperechoic areas of soft tissue injury or inflammation may suggest . Although plain radiography tends to be unproductive in diagnosing soft tissue injuries, certain radiographic findings are strongly suggestive of ligamentous, meniscal, or tendon damage. Particularly review the lateral radiograph for fluid within the suprapatellar pouch. The extensor tendon mechanism is normally well outlined.
Introduction. The detection and removal of embedded foreign bodies is often a difficult task, and foreign bodies within the soft-tissue are regularly undetected on first examination. 1 If undetected, there is a possibility of infection, long-term pain, deformities, and a reduction in functionality. 1 Wound trauma involving glass accounts for 13% of all cases . The detection and removal of embedded foreign bodies is often a difficult task, and foreign bodies within the soft-tissue are regularly undetected on first examination. 1 If undetected, there is a possibility of infection, long-term pain, deformities, and a reduction in functionality. 1 Wound trauma involving glass accounts for 13% of all cases presenting to the .
It depends on the amount of X-rays that penetrate the tissues. The soft tissues in the body (like blood, skin, fat, and muscle) allow most of the X-ray to pass through and appear dark gray on the film. A bone or a tumor, which is denser than soft tissue, allows few of the X-rays to pass through and appears white on the X-ray.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Soft tissue radiography requires special techniques because of the low________. a. imaging receptor contrast b. subject contrast c. part thickness d. spatial resolution, When doing soft tissue radiography, the differential absorption between ___ and ___ must be enhanced. a. bone, . Conventional radiography is the best modality for characterizing lesions that are depicted on bone scintiscans. . MRI provides good contrast resolution of bone and soft tissue and therefore has good sensitivity and specificity for detection for bone metastases. . This image shows heterogeneous enhancement of the soft tissue component of the .
how to test hardness of aluminum
different imaging tests explained
Resultado da 2 de mai. de 2014 · part time是把一个full time的工作分成几份由多个人来完成,part time的工作量工作时长一定少于同岗位full time,而casual是“零活儿”,按工时或按日付薪资,工作量和工作时长都可能比full time多的
which radiographic test shows soft tissue best|different types of radiology tests